Rooftop Solar Vs Open Access Solar: Which Is Right For Your Organisation?
Rooftop Solar Vs Open Access Solar: Which Is Right For Your Organisation?
As energy costs continue to rise and sustainability becomes a strategic priority, organizations across India are actively exploring solar power as a reliable and long-term solution. Solar energy not only reduces operational expenses but also strengthens a company’s environmental responsibility profile. Among the available options, Rooftop Solar and Open Access Solar have emerged as the two most impactful models for commercial and industrial consumers. While both serve the same purpose of clean energy generation, their implementation, scale, and benefits differ significantly.
Choosing between Rooftop Solar and Open Access Solar is not just a technical decision—it is a strategic one that impacts cost, scalability, regulatory involvement, and long-term energy planning. Understanding these models in detail helps organizations make informed investments that align with their operational and sustainability goals.
What Is Rooftop Solar?
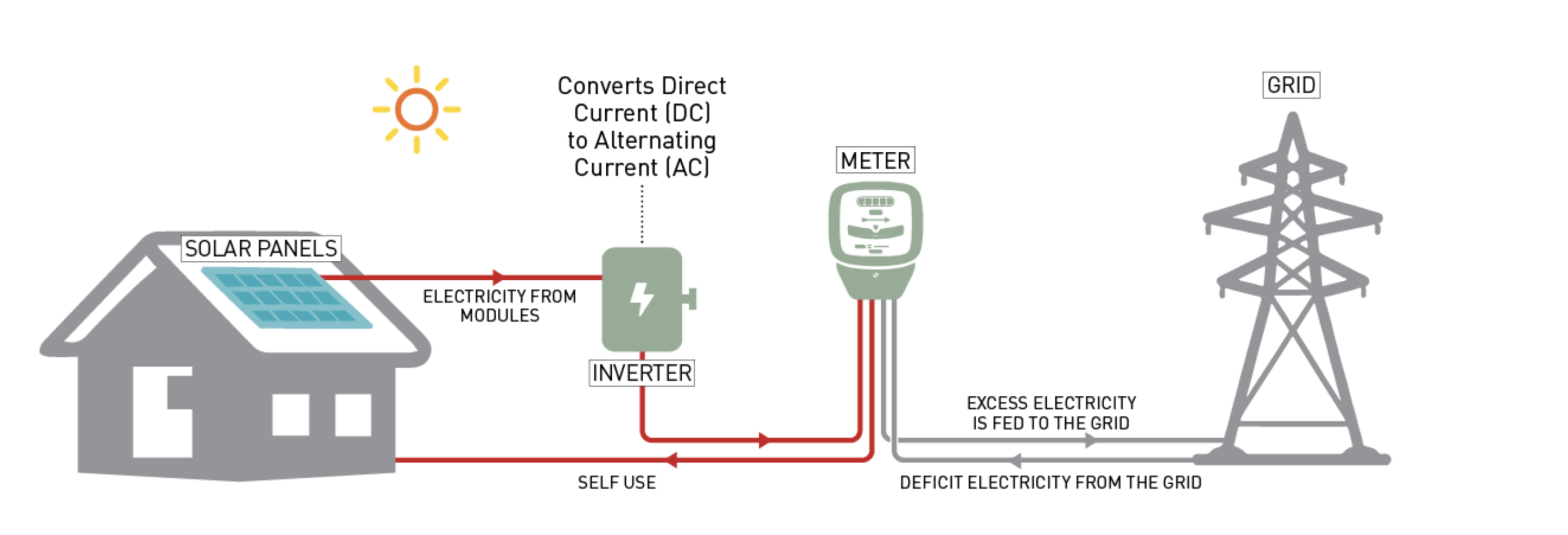
Rooftop solar refers to photovoltaic (PV) systems installed on the roof of a building where electricity is consumed. These systems generate power on-site and are connected directly to the facility’s electrical infrastructure. Surplus energy, if any, is exported to the grid through net metering or gross metering mechanisms, depending on state policies.
This model is particularly popular among factories, warehouses, commercial buildings, hospitals, and educational institutions that have ample roof space and steady daytime power consumption.
Key Advantages of Rooftop Solar:
- On-Site Power Generation
Electricity is produced exactly where it is needed, reducing transmission losses and dependence on grid supply. - Lower Electricity Bills
Rooftop systems significantly reduce power purchased from DISCOMs, resulting in long-term cost savings. - Government Support
Rooftop solar enjoys favorable government policies, incentives, and simplified regulatory approvals in most states. - Faster Implementation
Compared to large off-site solar projects, rooftop installations can be completed relatively quickly. - Strong Sustainability Branding
Visible solar installations showcase your organization’s commitment to renewable energy and responsible operations.
Limitations of Rooftop Solar:
- Capacity is restricted by available rooftop area.
- Structural strength and roof orientation must be assessed.
- Energy generation may not be sufficient for large industrial loads.
Rooftop solar works best for organizations with moderate energy requirements and suitable roof infrastructure.
What Is Open Access Solar?
Open Access Solar is a regulatory framework that allows large power consumers to buy electricity directly from a solar power generator located off-site, instead of purchasing it from the local DISCOM. The electricity is transmitted through the state grid to the consumer’s facility under a Power Purchase Agreement (PPA).
This model is ideal for energy-intensive industries that need solar power at a much larger scale than rooftop systems can provide.
Key Advantages of Open Access Solar:
- Large-Scale Power Availability
Open access solar can cater to high energy demands, often running into several megawatts. - Attractive Long-Term Tariffs
Businesses can lock in competitive tariffs for 10–25 years, protecting themselves from future grid tariff hikes. - No Rooftop Dependency
Energy generation does not depend on your building’s structure or space availability. - Supports Corporate Sustainability Goals
Open access solar allows companies to source a major portion of their energy from renewable sources, supporting ESG and net-zero targets.
Challenges with Open Access Solar:
- Regulatory approvals and compliance can be complex.
- Additional charges such as wheeling, transmission, cross-subsidy surcharge, and banking charges apply.
- Best suited for organisations with large connected loads, usually above 500 kW or 1 MW, depending on state regulations.
Rooftop Solar vs Open Access Solar: A Comparison
| Rooftop Solar | Open Access Solar |
Installation Location | On-site | Off-site solar plants |
Capacity | Limited by rooftop space | Highly scalable |
Investment Model | CAPEX / OPEX | Mostly OPEX through PPA |
Best Suited For | SMEs, offices, warehouses | Large industries, campuses |
Regulatory Complexity | Low | Medium to High |
Tariff Stability | Depends on grid policies | Long-term tariff certainty |
Sustainability Impact | Moderate to High | Very High |
Which One Should Your Organisation Choose?
Choose Rooftop Solar if:
- You have sufficient shadow-free rooftop area.
- Your electricity demand is moderate.
- You want quicker implementation and simpler approvals.
- You prefer asset ownership or partial energy independence.
Choose Open Access Solar if:
- Your power consumption is high and continuous.
- You need large-scale renewable energy integration.
- You want predictable energy costs over the long term.
- You have the administrative capability to manage regulatory processes.
The Hybrid Model: Best of Both Worlds
Many progressive organizations now adopt a hybrid solar strategy:
- Rooftop solar to maximize on-site generation.
- Open access solar to fulfill remaining energy requirements.
This approach ensures:
- Higher renewable penetration
- Optimal cost efficiency
- Better energy security
- Strong sustainability positioning
Why This Matters for Your Business
Solar adoption is no longer just about saving money—it is about resilience, sustainability, and future readiness. With rising power tariffs, tightening environmental regulations, and increasing stakeholder focus on ESG compliance, businesses that transition to solar energy gain a competitive advantage.
At Prabhat Renewable Energy & Agro Ltd, we help organisations evaluate, design, and implement the most suitable solar solutions—whether it is Rooftop Solar, Open Access Solar, or a combination of both. Our expertise ensures that your transition to renewable energy is seamless, compliant, and financially sound.